Your first Lambda function was a thing of beauty. Simple, elegant, it did one job and did it well. Then came the second. And the tenth. Before you knew it, you weren’t running an application; you were presiding over a digital ant colony, with functions scurrying in every direction without a shred of supervision.
AWS Lambda, the magical service that lets us run code without thinking about servers, can quickly devolve into a chaotic mess of serverless spaghetti. Each function lives happily in its own isolated bubble, and when demand spikes, AWS kindly hands out more and more bubbles. The result? An anarchic party of concurrent executions.
But don’t despair. Before you consider a career change to alpaca farming, let’s introduce three seasoned wranglers who will bring order to your serverless circus. These are the architectural patterns that separate the rookies from the maestros in the art of building resilient, scalable systems.
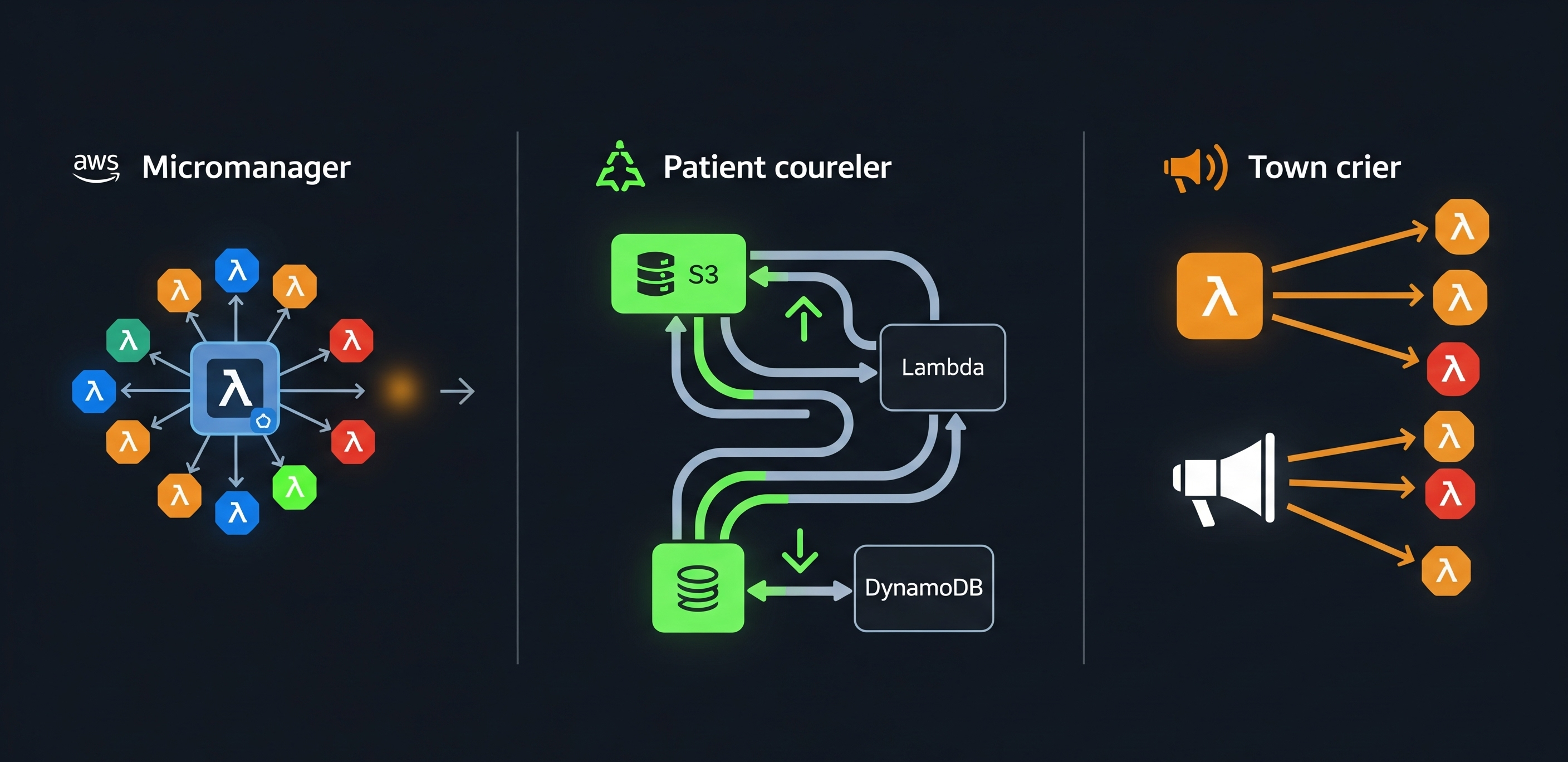
Meet the micromanager boss
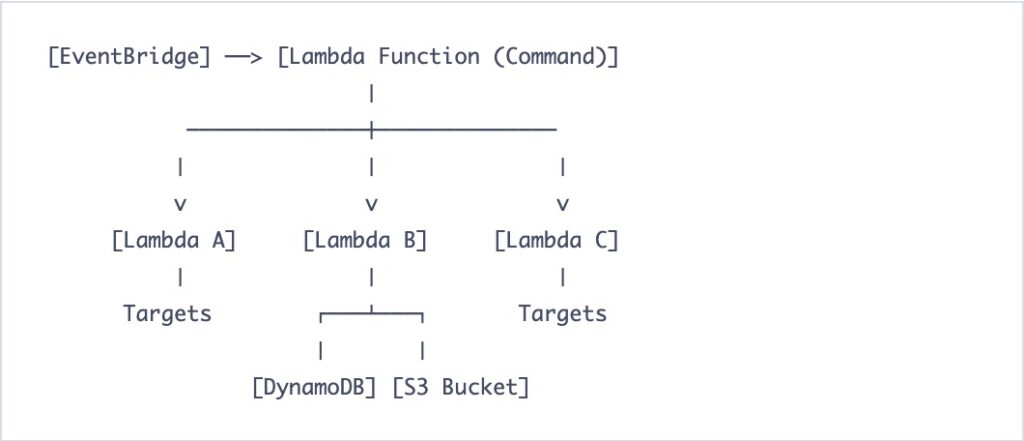
First up is a Lambda with a clipboard and very little patience. This is the Command Pattern function. Its job isn’t to do the heavy lifting—that’s what the interns are for. Its sole purpose is to act as the gatekeeper, the central brain that receives an order, scrutinizes it (request validation), consults its dusty rulebook (business logic), and then barks commands at its underlings to do the actual work.
It’s the perfect choice for workflows where bringing in AWS Step Functions would be like using a sledgehammer to crack a nut. It centralizes decision-making and maintains a crystal-clear separation between those who think and those who do.
When to hire this boss
- For small to medium workflows that need a clear, single point of control.
- When you need a bouncer at the door to enforce rules before letting anyone in.
- If you appreciate a clean hierarchy: one boss, many workers.
A real-world scenario
An OrderProcessor Lambda receives a new order via API Gateway. It doesn’t trust anyone. It first validates the payload, saves a record to DynamoDB so it can’t get lost, and only then does it invoke other Lambdas: one to handle the payment, another to send a confirmation email, and a third to notify the shipping department. The boss orchestrates; the workers execute. Clean and effective.
Visually, it looks like a central hub directing traffic:
Here’s how that boss might delegate a task to the notifications worker:
// The Command Lambda (e.g., process-order-command)
import { LambdaClient, InvokeCommand } from "@aws-sdk/client-lambda";
const lambdaClient = new LambdaClient({ region: "us-east-1" });
export const handler = async (event) => {
const orderDetails = JSON.parse(event.body);
// 1. Validate and save the order (your business logic here)
console.log(`Processing order ${orderDetails.orderId}...`);
// ... logic to save to DynamoDB ...
// 2. Delegate to the notification worker
const invokeParams = {
FunctionName: 'arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:send-confirmation-email',
InvocationType: 'Event', // Fire-and-forget
Payload: JSON.stringify({
orderId: orderDetails.orderId,
customerEmail: orderDetails.customerEmail,
}),
};
await lambdaClient.send(new InvokeCommand(invokeParams));
return {
statusCode: 202, // Accepted
body: JSON.stringify({ message: "Order received and is being processed." }),
};
};The dark side of micromanagement
Be warned. This boss can become a bottleneck. If all decisions flow through one function, it can get overwhelmed. It also risks becoming a “God Object,” a monstrous function that knows too much and does too much, making it a nightmare to maintain and a single, terrifying point of failure.
Enter the patient courier
So, what happens when the micromanager gets ten thousand requests in one second? It chokes, your system grinds to a halt, and you get a frantic call from your boss. The Command Pattern’s weakness is its synchronous nature. We need a buffer. We need an intermediary.
This is where the Messaging Pattern comes in, embodying the art of asynchronous patience. Here, instead of talking directly, services drop messages into a queue or stream (like SQS, SNS, or Kinesis). A consumer Lambda then picks them up whenever it’s ready. This builds healthy boundaries between your services, absorbs sudden traffic bursts like a sponge, and ensures that if something goes wrong, the message can be retried.
When to Call the Courier
- For bursty or unpredictable workloads that would otherwise overwhelm your system.
- To isolate slow or unreliable third-party services from your main request path.
- When you need to offload heavy tasks to be processed in the background.
- If you need a guarantee that a task will be executed at least once, with a safety net (a Dead-Letter Queue) for messages that repeatedly fail.
A Real-World Scenario
A user clicks “Checkout.” Instead of processing everything right away, the API Lambda simply drops an OrderPlaced event into an SQS queue and immediately returns a success message to the user. On the other side, a ProcessOrderQueue Lambda consumes events from the queue at its own pace. It reserves inventory, charges the credit card, and sends notifications. If the payment service is down, SQS holds the message, and the Lambda tries again later. No lost orders, no frustrated users.
The flow decouples the producer from the consumer:
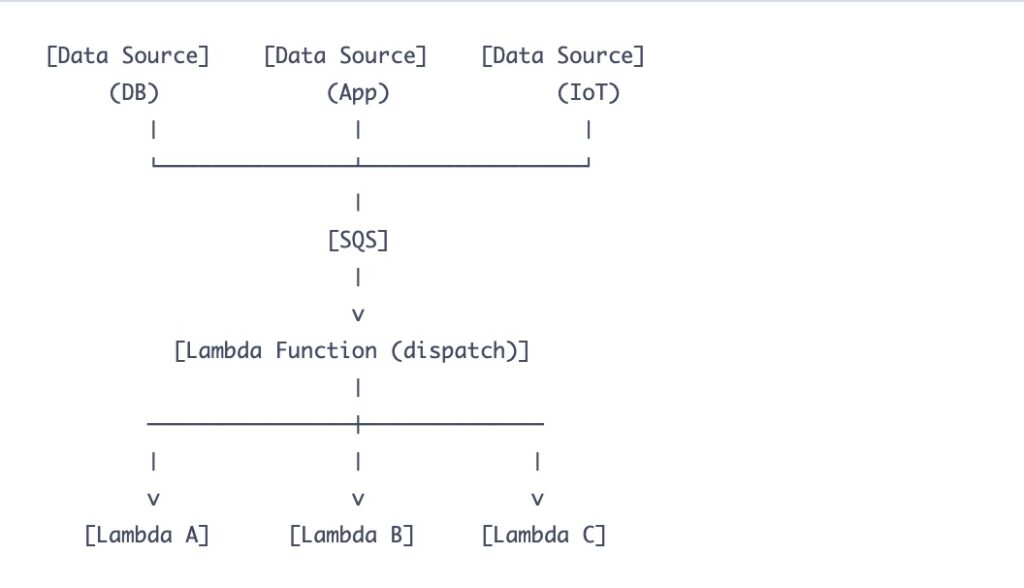
The producer just needs to drop the message and walk away:
// The Producer Lambda (e.g., checkout-api)
import { SQSClient, SendMessageCommand } from "@aws-sdk/client-sqs";
const sqsClient = new SQSClient({ region: "us-east-1" });
export const handler = async (event) => {
const orderDetails = JSON.parse(event.body);
const command = new SendMessageCommand({
QueueUrl: "[https://sqs.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/123456789012/OrderProcessingQueue](https://sqs.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/123456789012/OrderProcessingQueue)",
MessageBody: JSON.stringify(orderDetails),
MessageGroupId: orderDetails.orderId // For FIFO queues
});
await sqsClient.send(command);
return {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify({ message: "Your order is confirmed!" }),
};
};The price of patience
This resilience isn’t free. The biggest trade-off is added latency; you’re introducing an extra step. It also makes end-to-end tracing more complex. Debugging a journey that spans across a queue can feel like trying to track a package with no tracking number.
Unleash the Ttown crier
Sometimes, one piece of news needs to be told to everyone, all at once, without waiting for them to ask. You don’t want a single boss delegating one by one, nor a courier delivering individual letters. You need a proclamation.
The Fan-Out Pattern is your digital town crier. A single event is published to a central hub (typically an SNS topic or EventBridge), which then broadcasts it to any services that have subscribed. Each subscriber is a Lambda function that kicks into action in parallel, completely unaware of the others.
When to shout from the rooftops
- When a single event needs to trigger multiple, independent downstream processes.
- For building real-time, event-driven architectures where services react to changes.
- In high-scale systems where parallel processing is a must.
A real-world scenario
An OrderPlaced event is published to an SNS topic. Instantly, this triggers multiple Lambdas in parallel: one to update inventory, another to send a confirmation email, and a third for the analytics pipeline. The beauty is that the publisher doesn’t know or care who is listening. You can add a fifth or sixth subscriber later without ever touching the original publishing code.
One event triggers many parallel actions:
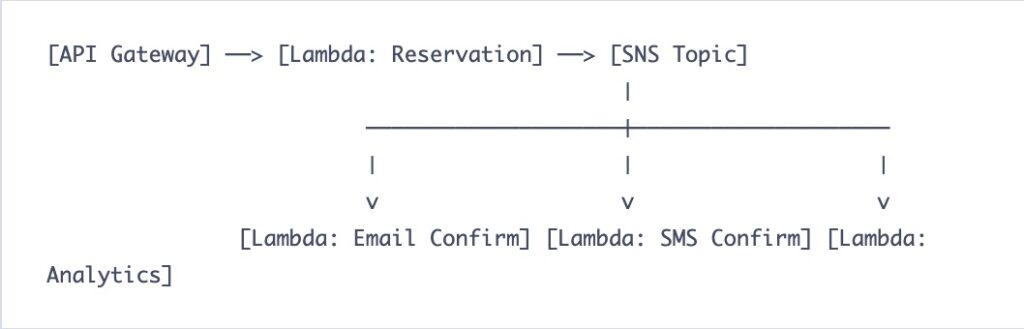
The publisher’s job is delightfully simple:
// The Publisher Lambda (e.g., reservation-service)
import { SNSClient, PublishCommand } from "@aws-sdk/client-sns";
const snsClient = new SNSClient({ region: "us-east-1" });
export const handler = async (event) => {
// ... logic to create a reservation ...
const reservationDetails = {
reservationId: "res-xyz-123",
customerEmail: "jane.doe@example.com",
};
const command = new PublishCommand({
TopicArn: "arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:123456789012:NewReservationsTopic",
Message: JSON.stringify(reservationDetails),
MessageAttributes: {
'eventType': {
DataType: 'String',
StringValue: 'RESERVATION_CONFIRMED'
}
}
});
await snsClient.send(command);
return { status: "SUCCESS", reservationId: reservationDetails.reservationId };
};The dangers of a loud voice
With great power comes a great potential for a massive, distributed failure. A single poison-pill event could trigger dozens of Lambdas, each failing and retrying, leading to an invocation storm and a bill that will make your eyes water. Careful monitoring and robust error handling in each subscriber are non-negotiable.
Choosing your champions
There you have it: the Micromanager, the Courier, and the Town Crier. Three patterns that form the bedrock of almost any serverless architecture worth its salt.
- Use the Command Pattern when you need a firm hand on the tiller.
- Adopt the Messaging Pattern to give your services breathing room and resilience.
- Leverage the Fan-Out Pattern when one event needs to efficiently kickstart a flurry of activity.
The real magic begins when you combine them. But for now, start seeing your Lambdas not as a chaotic mob of individual functions, but as a team of specialists. With a little architectural guidance, they can build systems that are complex, resilient, and, best of all, cause you far fewer operational headaches.